
Ocean temperatures on the east coasts of major continents are generally warmer than on their west coasts. This is due to the influence of ocean currents and wind patterns.
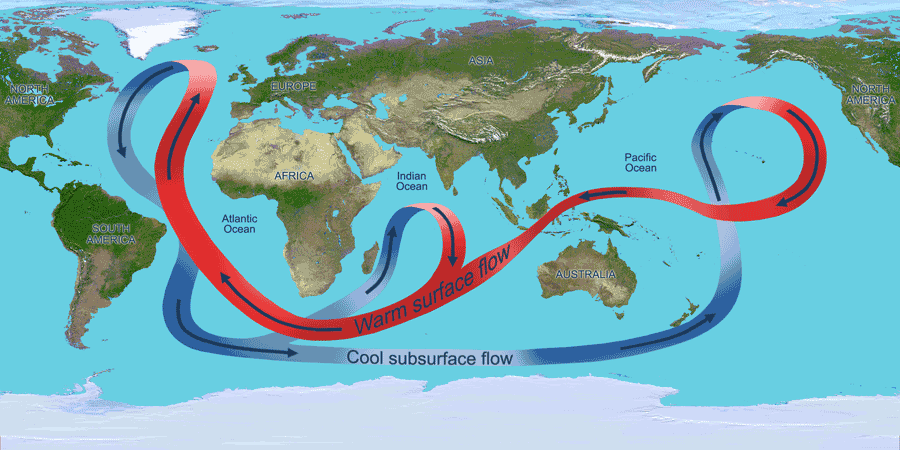
Ocean temperatures vary significantly between the east and west coasts of major continents. Warm currents, such as the Gulf Stream, flow along the east coasts, raising temperatures. On the west coasts, cold currents like the California Current lead to cooler temperatures.
This temperature difference impacts local climates, marine biodiversity, and weather patterns. Coastal regions on the east side typically experience warmer and more humid conditions, while west coast regions tend to be cooler and drier. Understanding these temperature variations is crucial for climate studies, marine navigation, and coastal management.
Credit: www.visualcapitalist.com
Introduction To Ocean Temperatures
Understanding ocean temperatures is crucial for studying marine life and climate.
Ocean temperatures vary significantly between the East and West Coasts of major continents.
These variations affect weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and local climates.
Global Ocean Patterns
Ocean currents play a vital role in distributing heat across the globe.
Warm currents flow from the equator towards the poles.
Cold currents move from the poles towards the equator.
This movement creates distinct temperature zones.
On the East Coast, warm currents like the Gulf Stream influence temperatures.
On the West Coast, cold currents like the California Current dominate.
These currents create a stark contrast in ocean temperatures.
Factors Affecting Ocean Temperatures
Several factors influence ocean temperatures on different coasts.
One key factor is the direction of ocean currents.
Warm currents heat the water, while cold currents cool it.
Wind patterns also affect ocean temperatures.
Winds can push warm or cold water towards the coast.
Coastal geography, such as the presence of mountains or bays, also plays a role.
Here is a table summarizing the main factors:
| Factor | Effect on Ocean Temperature |
|---|---|
| Ocean Currents | Warm or cool water movement |
| Wind Patterns | Push warm or cold water |
| Coastal Geography | Influences water movement |
Credit: www.ces.fau.edu
East Coast Ocean Temperatures
The ocean temperatures on the East Coast of major continents are fascinating. These temperatures influence the climate, marine life, and local weather patterns. Understanding these temperatures helps in predicting weather and planning activities. Let’s dive into the typical climate conditions and seasonal variations.
Typical Climate Conditions
The East Coast often experiences warm ocean currents. This affects the climate of nearby lands. For instance:
| Continent | Ocean Current | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Gulf Stream | 15 – 30 |
| South America | Brazil Current | 18 – 28 |
| Africa | Agulhas Current | 20 – 28 |
| Australia | East Australian Current | 22 – 30 |
The warm currents lead to humid climates on the East Coast. This impacts the local weather significantly.
Seasonal Variations
Seasonal changes impact ocean temperatures greatly. Here’s a brief look:
- Winter: Ocean temperatures drop but remain relatively mild.
- Spring: Temperatures begin to rise, preparing for summer.
- Summer: The warmest period, with temperatures peaking.
- Autumn: Gradual cooling as winter approaches.
In North America, summer ocean temperatures can reach up to 30°C. During winter, they may drop to around 15°C. On the East Coast of Australia, summer temperatures can soar to 30°C, while winter sees a mild 22°C.
Understanding these seasonal variations is key. It helps in planning coastal activities and understanding climate patterns.
West Coast Ocean Temperatures
The ocean temperatures on the west coast of major continents are fascinating. These temperatures vary due to several factors. Let’s explore these in detail.
Prevailing Climate Features
The west coast of continents often experiences unique climate features. These include cool currents and coastal upwelling. The cool currents bring cold water from polar regions. This makes the west coast waters cooler.
Coastal upwelling is another key factor. Wind patterns push surface water away from the coast. This allows cold, nutrient-rich water to rise. This process further cools the ocean temperatures.
Annual Temperature Changes
Annual temperature changes on the west coast are also noteworthy. Here is a table showing average temperatures for different months:
| Month | Average Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| January | 10 |
| April | 14 |
| July | 18 |
| October | 16 |
From January to July, temperatures gradually rise. The peak is in July with 18°C. From July to October, temperatures slightly decrease. This cycle repeats annually.
These changes impact marine life and coastal climates. Cooler waters lead to more marine productivity. They also create unique weather patterns.
Influence Of Currents
The temperatures of the ocean vary greatly due to the influence of currents. These currents play a vital role in determining the climate and marine life of coastal regions. Here, we will explore how these currents affect the ocean temperatures on the East and West Coasts of major continents.
Gulf Stream Impact
The Gulf Stream is a powerful ocean current. It flows from the Gulf of Mexico up the East Coast of North America. This current brings warm water from the tropics to the north. As a result, the ocean temperatures on the East Coast are generally warmer.
Let’s look at a comparison:
| Region | Ocean Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| Florida | 24-30 |
| New York | 10-20 |
| Canada (East Coast) | 2-10 |
The warm water of the Gulf Stream affects the climate. It also supports diverse marine life. Many species thrive in these warm waters.
California Current Effects
The California Current flows along the West Coast of North America. It brings cold water from the north to the south. This current significantly cools the ocean temperatures along the West Coast.
Here is a comparison:
| Region | Ocean Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|
| California | 10-20 |
| Oregon | 8-14 |
| Washington | 7-12 |
The cold water of the California Current affects marine life. Species adapted to cold water thrive here. The climate is also cooler compared to the East Coast.
East Vs. West Coast: Tropical Regions
In the tropical regions, the ocean temperatures vary significantly between the east and west coasts of major continents. This variation impacts the climate, marine life, and ecosystems in these areas. Understanding these differences helps in grasping the broader implications of oceanic patterns.
Temperature Differences
The east coast of tropical regions often experiences warmer ocean temperatures. This is due to the presence of warm ocean currents. For instance, the Gulf Stream affects the east coast of North America, making waters warmer.
On the west coast, the temperatures are typically cooler. This happens because of cold ocean currents. The California Current cools the west coast of North America. This pattern is seen in other continents too.
| Continent | East Coast Temp (°C) | West Coast Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 25-30 | 15-20 |
| South America | 26-28 | 15-19 |
| Africa | 27-29 | 18-22 |
| Asia | 28-30 | 20-24 |
Impact On Marine Life
The warmer waters on the east coasts support diverse marine ecosystems. Coral reefs thrive in these warm temperatures. Tropical fish species are abundant here.
In contrast, the cooler waters on the west coasts are rich in nutrients. These nutrients support large populations of plankton. This attracts bigger marine animals like whales and sharks.
- Coral Reefs: Found on east coasts.
- Plankton Blooms: Common on west coasts.
- Marine Biodiversity: Higher in warmer waters.
- Large Marine Animals: Frequent in nutrient-rich cooler waters.
Both coasts play vital roles in maintaining marine biodiversity. The differences in temperature create unique habitats. Understanding these patterns helps in conservation efforts.

Credit: insideclimatenews.org
East Vs. West Coast: Polar Regions
The polar regions of the world exhibit stark differences in ocean temperatures between the east and west coasts. These differences impact the environment, sea ice formation, and marine life. By understanding these contrasts, we can better appreciate the unique characteristics of each polar region.
Temperature Contrasts
The east coasts of polar regions tend to be warmer. This is due to the presence of warm ocean currents. These currents move from the equator towards the poles. On the west coasts, cooler ocean currents prevail. These currents flow from the polar regions towards the equator.
Here is a table summarizing these temperature contrasts:
| Region | East Coast Temperature | West Coast Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Arctic | Warmer | Cooler |
| Antarctica | Warmer | Cooler |
Influence On Sea Ice
The temperature differences greatly affect sea ice formation. Warmer waters on the east coasts delay sea ice formation. This leads to thinner ice sheets. In contrast, the cooler waters of the west coasts promote faster ice formation. This results in thicker and more extensive ice coverage.
Consider these points:
- East coasts have shorter ice seasons.
- West coasts experience longer ice seasons.
- Ice on the east coasts is often more fragmented.
- West coast ice is usually denser and more stable.
These differences impact local ecosystems and human activities. Understanding them is crucial for navigating these icy waters safely.
Human Activities And Coastal Temperatures
The ocean temperatures on the East and West Coasts of major continents vary significantly due to various factors. One crucial factor is human activities. Activities like pollution and coastal development have a significant impact on these temperatures.
Pollution Effects
Pollution plays a major role in changing ocean temperatures. Industries discharge waste into coastal waters. This waste can raise temperatures. Warmer water impacts marine life negatively. Fish and coral reefs suffer from higher temperatures.
Oil spills are another concern. They create a film on the water surface. This film absorbs more heat from the sun. As a result, the ocean temperature increases. Chemicals from agriculture also reach the oceans. They cause harmful algal blooms. These blooms can trap heat and raise water temperatures.
Coastal Development Impact
Coastal development also affects ocean temperatures. Construction of buildings and roads near coasts disrupts natural habitats. This causes changes in water flow and temperature.
Urbanization leads to increased runoff. Runoff carries heat and pollutants into the ocean. This process elevates ocean temperatures. Seawalls and other structures can also change water currents. These changes impact the temperature balance of coastal waters.
Tourism activities contribute as well. More people mean more waste and pollution. This leads to higher ocean temperatures, affecting marine ecosystems.
Future Trends In Ocean Temperatures
The future trends in ocean temperatures are crucial for our planet. Both the East and West Coasts of major continents face unique challenges. Rising ocean temperatures can impact marine life and weather patterns. Understanding these trends can help us prepare for the future.
Climate Change Projections
Climate change is causing ocean temperatures to rise globally. Scientists use models to predict future trends. These models show significant warming on both coasts. The East Coast generally warms faster due to its geography. The West Coast may see slower but steady increases in temperature.
Here is a comparison table of projected temperature increases for major continents:
| Continent | East Coast Increase (°C) | West Coast Increase (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 2.5 | 1.8 |
| South America | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| Europe | 2.0 | 1.6 |
| Africa | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| Asia | 2.4 | 1.9 |
Potential Impacts On Coasts
Rising ocean temperatures affect coastal ecosystems. Warmer waters can lead to coral bleaching. This harms marine habitats and biodiversity. Fish populations may migrate, seeking cooler waters. This can impact local fisheries and economies.
Here are some potential impacts:
- Increased coastal erosion
- More frequent and severe storms
- Rising sea levels
- Changes in marine species distribution
Communities on both coasts need to adapt. Building resilient infrastructure can help mitigate these impacts. Governments must also invest in scientific research and monitoring. Understanding future trends helps us prepare for a warming world.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Ocean Temperatures Vary On The East Coast?
Ocean temperatures on the East Coast are generally warmer. This is due to the Gulf Stream. The Gulf Stream brings warm water from the tropics up the coast.
Why Are West Coast Ocean Temperatures Colder?
West Coast ocean temperatures are colder because of the California Current. The California Current brings cold water from the northern Pacific Ocean.
Do Ocean Temperatures Affect Marine Life?
Yes, ocean temperatures significantly impact marine life. Different species thrive in specific temperature ranges. Warmer waters support different ecosystems than colder waters.
Are East Coast Beaches Warmer Than West Coast Beaches?
Yes, East Coast beaches are generally warmer. The Gulf Stream influences the warmer temperatures. West Coast beaches are cooler due to the California Current.
Conclusion
Understanding ocean temperature differences is crucial for marine life and coastal activities. East Coast waters tend to be warmer due to currents. West Coast waters are cooler, influenced by cold ocean currents. These variations impact local climates and ecosystems. Knowing these differences helps in planning activities and conservation efforts.

